Fast-Moving Consumer Goods (FMCG) have become an integral part of our daily lives, surrounding us in every aspect. This industry has been instrumental in driving economic success, but it now faces significant pressure to adapt to evolving consumer needs in order to maintain market presence. With changing fashion, technology, trends, lifestyles, disposable income, and other factors, consumer behavior and channel landscapes are also evolving. This presents a formidable challenge for FMCG companies, requiring them to exert maximum effort to uphold their brand legacy and secure a place on every household’s and consumer’s preference list. Let’s delve into this article to gain insights into the FMCG business, its economic significance, the challenges it confronts, and its future prospects.

What is FMCG?
FMCG stands for Fast-Moving Consumer Goods, also known as Consumer Packaged Goods (CPG). FMCG products are designed for frequent use and are sold in high-volume, quickly, and at a relatively cheaper rate. They are termed ‘fast moving’ because they have a short shelf life or are perishable items requiring continuous stocking and replenishment.
Fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG) are non-durable by nature, have a huge demand and are affordable for mostly everyone. They are essential items that are frequently purchased by consumers to meet their daily needs and are readily available in various retail channels, including nearby retail shops, supermarkets, hypermarkets, convenience stores, and online platforms.
Categories in FMCG
FMCG products are essential items that play a significant role in fulfilling the daily needs of individuals. They encompass a wide range of goods that are consumed on a regular basis by consumers. These products can be conveniently categorized as follows:
- Processed foods: Noodles, cereals, and boxed pasta
- Prepared meals: Ready-to-eat meals
- Beverages: Bottled water, energy drinks, and juices
- Baked goods: Cookies, bread, and doughnuts
- Fresh foods, frozen foods, and dry goods: Milk, Fruits, vegetables, Ice creams, and nuts
- Medicines: Aspirin, pain relievers, masks, and other general medications
- Cleaning products: Tissue paper, oven cleaner, and window and glass cleaner
- Cosmetics and toiletries: Hair care products, toothpaste, and soap
- Office supplies: Pens, pencils, and markers
The top FMCG (or CPG) companies include Procter & Gamble, Johnson & Johnson, Nestle, Unilever, JBS, L’Oréal along with beverage companies like Coca Cola, Pepsi etc. There are various factors considered while ranking the FMCG companies such as Revenue, Profitability, Brand Strength, Innovation and Global reach.

Importance of FMCG in the Economy
The FMCG industry is a crucial and integral part of the global economy, making significant contributions to a country’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP) and employment generation. In a developing country like India, FMCG sector contributes to about 10% of the total GDP and provides employment to about 10 million people. Here are some specific examples of how FMCG contributes to economic growth:
1. Tax revenue: The FMCG sector generates billions of dollars in tax revenue for governments around the world. This revenue can be used to fund essential services such as education, healthcare, and infrastructure
2. Job creation: The FMCG sector is a major employer, providing jobs across the supply chain, from manufacturing to distribution to retail and marketing. This sector employs millions of people around the world, and it is a major source of income for many families.
3. Ancillary industries: The FMCG sector also boosts ancillary industries, such as packaging, logistics, marketing, and advertising. These industries provide goods and services to the FMCG sector, and they also create jobs and generate economic activity.
4. Innovation and technology: The FMCG sector is constantly innovating and adopting new technologies. This helps to keep the sector competitive, and it also creates new opportunities for jobs and businesses. For example, the rise of e-commerce has created new opportunities for FMCG companies to reach consumers.
FMCG companies strive to establish themselves as household names, targeting vast audiences across different geographic regions and socioeconomic segments. Their goal is to reach a significant consumer base, spanning various tiers of cities, states, and countries. By targeting a broad audience, FMCG companies aim to become an integral part of the consumption patterns of millions of households. A thriving FMCG sector is often a sign of strong consumer confidence and increased spending essential for sustained economic growth giving rise to innovation and technological advancements.
Challenges in the FMCG Sector
The FMCG sector is highly challenging, characterized by fierce competition. The cut-throat competition, makes it essential for companies to constantly strive to differentiate themselves and gain a competitive edge. Balancing supply and demand is a significant challenge in this industry. Additionally, FMCG companies typically operate on slim profit margins, typically ranging from 5% to 25%. Therefore 100’s of brands enter the FMCG industry every year and 100’s of brand leave the industry within a year. Due to managing these factors effectively requires careful attention to various considerations:
Resilient Supply Chain: FMCG companies face sector-specific challenges, particularly in logistics management. Meeting tight deadlines, managing increasing stock levels, and ensuring supplier proximity, traceability, and security are crucial. Failure to optimize the supply chain can result in substantial cost implications, such as dead stock and financial losses. Unavailability of a product when demand is high in any segment can make the customer go for other product which increases the chances of loosing the customer sometimes forever.
Presence in all Distribution Channels: FMCG products, being household necessities, must be available across physical, digital, and online distribution channels. Ensuring a widespread presence enhances accessibility and caters to diverse consumer preferences and shopping habits. This requires capital investment along with marketing in order to maintain your presence and capture the maximum market share.

Competitive Price and Diverse Range of Products: Pricing plays a crucial role in the FMCG industry, where consumers often compare prices and seek the best value for their money. Offering competitive pricing and attractive discounts can attract customers and drive sales volume. Recognizing that consumers have varying purchasing power and preferences, FMCG companies strive to offer products in different sizes and price formats. This ensures affordability and accommodates individual and family needs, ultimately expanding the consumer base to each and every category of consumers.
Marketing, Customer Acquisition & Customer Retention: Effective marketing strategies are vital for FMCG companies. They need to create brand awareness, engage consumers, and promote their products. Investments in advertising, promotions, and brand building activities are necessary to gain visibility and maintain competitiveness. Acquiring new customers is a constant focus. FMCG companies achieve this by implementing targeted marketing campaigns, expanding distribution networks, and understanding consumer behavior to attract new customers and expand market share. Additionally, customer retention is crucial. Maintaining customer trust and satisfaction plays a vital role in retaining customers. Negative reviews, media coverage, or customer dissatisfaction can result in customer attrition, leading to significant business losses. Losing a customer in any segment is not affordable for the company.
FMCG’s Future: Market Expansion and Growth Opportunities
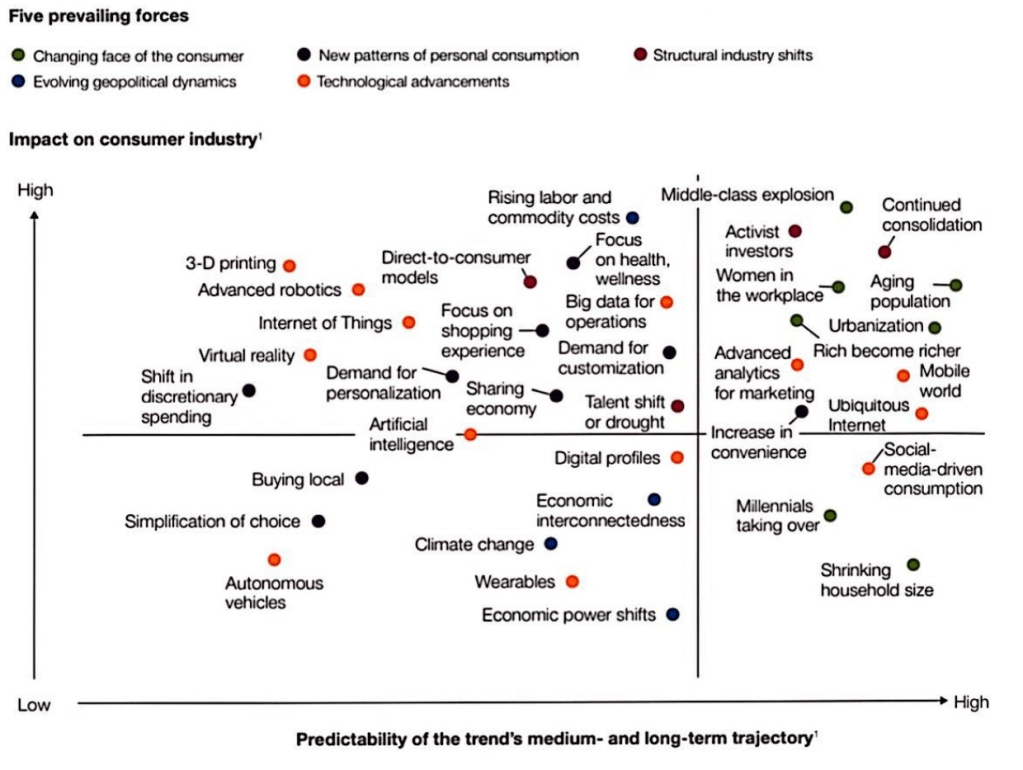
There is a significant level of consensus among industry observers regarding the projected evolution of certain trends in the next 15 years. One key expectation is that middle-class consumer spending on a global scale will nearly triple by 2030, with emerging markets driving the growth momentum while developed markets may witness relatively stagnant growth. Additionally, it is widely anticipated that mobile phone ownership will extend to more than 75 percent of the world’s population. According to the various reports, it is forecasted that FMCG market can grow at rate of minimum 5% every year till 2030. There are various factors contributing to the growth of this sector such as:
Changing face of the consumer: Rapid urbanization, rising disposable incomes leading to the growing number of middle class, aging population, shrinking household size, Millennials and Gen Z taking over is leading to an increase in demand for FMCG products. Companies that can successfully tap into these markets, adapt to local preferences, and offer affordable options may witness significant growth.
Evolving geopolitical dynamics: Geopolitical shifts, such as the signing of free trade agreements or the easing of trade barriers, can open up new markets and create opportunities for FMCG companies to expand their operations globally. Access to larger consumer bases can drive significant growth for FMCG products introducing a new shift in the consumer behavior and preferences.
Technological advancements: The FMCG sector is expected to be influenced by emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, robotics, automation, 3-D printing and the Internet of Things (IoT). These technologies can improve supply chain efficiency, enhance product development and customization, and enable targeted marketing strategies.
Personalization and customization: Consumers are increasingly focused on health-conscious choices and sustainability. This trend is likely to continue, with a greater emphasis on organic, natural, and sustainable products. They are seeking personalized experiences and products tailored to their specific needs. FMCG companies that can offer customizable options and engage consumers through personalized marketing campaigns are expected to thrive in the future market.
Data-driven decision making: As data collection and analysis capabilities improve, FMCG companies will increasingly rely on data-driven insights to make informed business decisions. Utilizing consumer data can help companies understand consumer behavior, preferences, and market trends, allowing them to optimize their product offerings and marketing strategies.
In conclusion, the total addressable market (TAM) for FMCG companies is directly tied to population size, as the need for essential daily items drives demand. With an ever-increasing number of people, the potential customer base for FMCG companies expands accordingly. Moreover, the rising demand for convenience and luxury in the fast-paced, modern lifestyle further propels the growth of FMCG products. To thrive in this competitive landscape, FMCG companies must adeptly navigate market dynamics, comprehend consumer behavior, and implement robust business strategies. By doing so, they can position themselves at the forefront of the FMCG industry and effectively meet the evolving demands of consumers. As the future unfolds, it will be intriguing to witness how these companies fiercely compete, constantly pushing boundaries to maintain their dominance in the FMCG sector.
“A customer is the most important visitor on our premises, he is not dependent on us. We are dependent on him. He is not an interruption in our work. He is the purpose of it. He is not an outsider in our business. He is part of it. We are not doing him a favor by serving him. He is doing us a favor by giving us an opportunity to do so.”
– Mahatma Gandhi