As India aspires to become a global manufacturing hub and economic powerhouse, adopting vertical integration emerges as a pivotal strategy for success. With its expansive market potential and strategic geographic location, India is well-positioned to capitalize on the global demand for diverse manufacturing capabilities. By adopting vertical integration, Indian firms can strengthen their manufacturing processes, operational efficiency, drive innovation, and secure a competitive edge. This article explores why vertical integration is crucial for India’s manufacturing sector.

What is Vertical Integration?
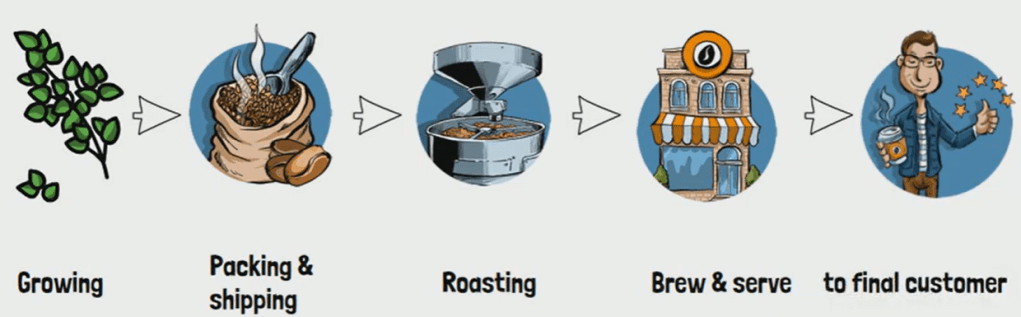
Vertical Integration is a business strategy where a company controls multiple stages of its supply chain—from raw material procurement to production, distribution, and sales. By integrating these stages, companies aim to streamline operations, reduce costs, and enhance efficiency, ultimately gaining a competitive edge in the market.
For example, Starbucks uses vertical integration by managing various parts of its coffee business. Instead of just purchasing coffee beans, Starbucks buys and manages coffee farms, roasts beans in-house, and controls distribution and sales through its own cafes. This integration ensures high quality, reduces costs, and maintains product consistency.
Vertical Integration can be divided into two types:
Backward Integration involves controlling activities earlier in the supply chain. This can lead to lower costs, better quality, and more reliable supply. For instance, Amazon.com evolved from an online book retailer to controlling its own publishing and production processes, exemplifying backward integration.
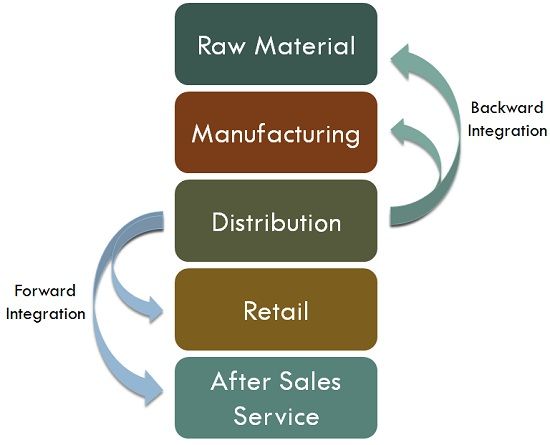
Forward integration is where a company expands its activities to include control over the direct distribution of its products. DMart, for example, manages its own lands, stores, distribution from warehouses, and logistics. This helps DMart ensures efficiency in delivering products to the end consumer, maintaining control over retail operations, profit margins and enhancing customer experience.
Why Vertical Integration is crucial for India?
Vertical integration is crucial for Indian companies, particularly in the burgeoning e-commerce market, as it streamlines operations by controlling multiple stages of production and distribution. This strategy reduces costs by eliminating intermediary expenses and addressing fragmented supply chains and unreliable suppliers. It enhances quality control, fosters faster innovation, and enables quicker adaptation to market demands. Supported by initiatives like Make in India and Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) schemes, vertical integration boosts efficiency, lowers costs, better inventory management and improves delivery speed, leading to competitive pricing and superior customer service. This approach provides a significant strategic advantage in India’s competitive and evolving market landscape by reducing logistical challenges and enhancing overall market positioning.
China has achieved global dominance as the “World’s Factory” by exerting extensive control over its supply chain, which has enhanced cost efficiency, quality control, and supply chain reliability. Companies like Haier, BYD, and Huawei exemplify this success through their control over production processes, from raw material procurement to final assembly. BYD’s dominance in battery and electric vehicle manufacturing and Huawei’s in-house chip design and smartphone production highlight how vertical integration drives innovation and competitiveness. With supportive government policies, these integrated firms have scaled quickly and accessed global markets, solidifying China’s manufacturing leadership. India’s path to similar success could lie in embracing vertical integration to enhance its manufacturing capabilities.
Vertical integration presents several challenges for Indian companies: substantial upfront investment, complex management, potential resource strain, and the need for high-level expertise to avoid inefficiencies.
Indian Companies that have adopted Vertical Integration
Several giant multinational companies, including Apple, Amazon, Coca-Cola, Tesla, and Zara, have successfully implemented vertical integration, reaping significant benefits such as optimized operations, substantial cost reductions, and enhanced quality and market control. This strategic approach has not only driven continuous growth and innovation but also solidified their positions as formidable leaders in their respective markets. By controlling multiple stages of their supply chains, these companies have achieved greater efficiency and competitive advantage, setting a powerful example for others aiming to excel in their industries.
Tata Group: The Tata Group has implemented vertical integration across its various sectors. For instance, Tata Steel controls the entire value chain from iron ore mining to steel production and distribution. This control allows Tata Steel to manage costs effectively, ensure consistent quality, and maintain a reliable supply chain, giving it a competitive edge in the steel industry.
Reliance Industries: In petrochemicals, Reliance controls the entire process from crude oil refining to producing end products like plastics and synthetic fibers. This integration ensures cost efficiency and supply stability. Similarly in the telecommunications, Reliance Jio owns the network infrastructure and provides mobile services, enabling seamless control over quality and customer experience.
Adani Group: Adani Ports & SEZ manages the logistics for Adani Power, ensuring a steady coal supply for its power plants. Adani Enterprises operates coal mines to supply its power plants, reducing reliance on external suppliers. The group also integrates its cement business with its real estate arm, optimizing the supply chain and reducing costs.
Sectors Benefiting from Vertical Integration
Sectors like automotive, e-commerce, FMCG, pharmaceuticals, and textiles in India benefit greatly from vertical integration. Automotive firms streamline production and ensure quality by managing all stages from components to assembly. FMCG companies enhance inventory management and distribution efficiency. Pharmaceuticals achieve better compliance and quality control, while textiles optimize production and material quality by integrating sourcing with manufacturing and distribution. This approach fosters sustainable growth and boosts sector competitiveness in both domestic and international markets.
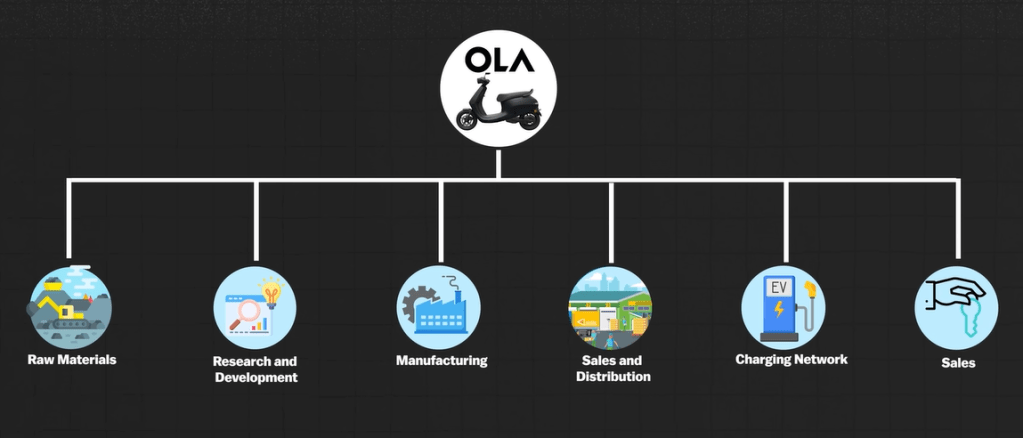
Ola Electric is strategically focusing on vertical integration to bolster its position in the Indian electric vehicle (EV) market. By investing in its own manufacturing facility, Ola ensures control over the entire production process of electric scooters, enhancing quality and reducing costs. The company is also developing its own network of charging stations to streamline the charging experience for customers. Additionally, Ola integrates proprietary technology into its vehicles, including advanced software for vehicle management. Despite challenges such as limited access to crucial raw materials like lithium and cobalt, and a smaller production scale, Ola’s significant investments in R&D and its Gigafactory for battery manufacturing highlight its commitment to overcoming these hurdles. This comprehensive vertical integration approach aims to improve operational efficiency, leverage government subsidies, and achieve economies of scale, positioning Ola for success in the competitive EV landscape.
Conclusion
As India’s manufacturing sector continues to grow, adopting vertical integration can unlock new levels of innovation and productivity. With supportive government policies and a robust market potential, companies that strategically embrace this model will likely gain a substantial competitive edge. On a macroeconomic scale, it spurs job creation and economic growth through investments in local infrastructure and supply chains. Vertical integration is not merely a strategy; it is a pathway to driving sustained growth, achieving operational excellence, and solidifying India’s position as a formidable player in the global manufacturing arena.
“Vertical integration is a strategic lever that can transform a company’s ability to innovate, streamline operations, and dominate its market by controlling every stage of the value chain.”
– Vedant Kale