Semiconductor chips have emerged as indispensable components of the global economy, underpinning the digital revolution and serving as the cornerstone for the advancement of AI technology. With recent advancements in AI and IoT, the demand for semiconductors has skyrocketed creating national interest and fundamental manufacturing need worth trillions of dollars. Let’s delve into this article to understand how the chip industry will steer the AI revolution.
Semiconductors bridge the gap between the properties of insulators and metals, offering a unique electrical conductivity essential to modern technology. Semiconductor chips, made from thin silicon slices, contain various components arranged in precise patterns. Components like transistors manage the flow of electricity within the circuit, enabling essential computing functions such as memory and logic. Memory chips handle storing and retrieving data, while logic chips act as the brain, processing information to perform tasks.
In 1965, Gordon E. Moore, co-founder of Intel, formulated Moore’s Law, an observation that the number of transistors on a microchip roughly doubles every two years, exponentially increasing the computing power whereas its costs is halved over the same timeframe.
Moore’s Law has been a guiding force in tech for over 50 years, but recent advancements have sparked debates on its sustainability due to its physical constraints and manufacturing complexities, casting doubt on its future viability.
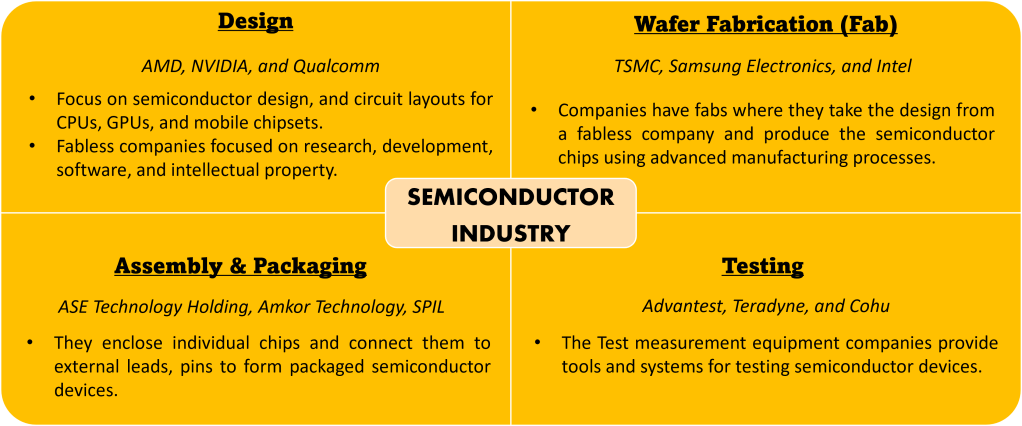
How is the Semiconductor Industry divided?
Global competition for Chip Manufacturing
Amidst surging global demand for advanced devices, the importance of semiconductors has become increasingly apparent, especially since the COVID-19 pandemic. The semiconductor industry faced turbulent times in the early 2020s, with factors like the pandemic, trade tensions between China and the US, and conflicts in Ukraine causing significant disruptions to the supply chain. Despite soaring demand, semiconductor manufacturers struggled to meet production and shipping demands, resulting in a worldwide shortage that persists today.
Today, Asia accounts for over 75% of the global semiconductor fab capacity, with an even higher market share of 90% in chip assembly and testing. This includes countries like China, Taiwan and South Korea.
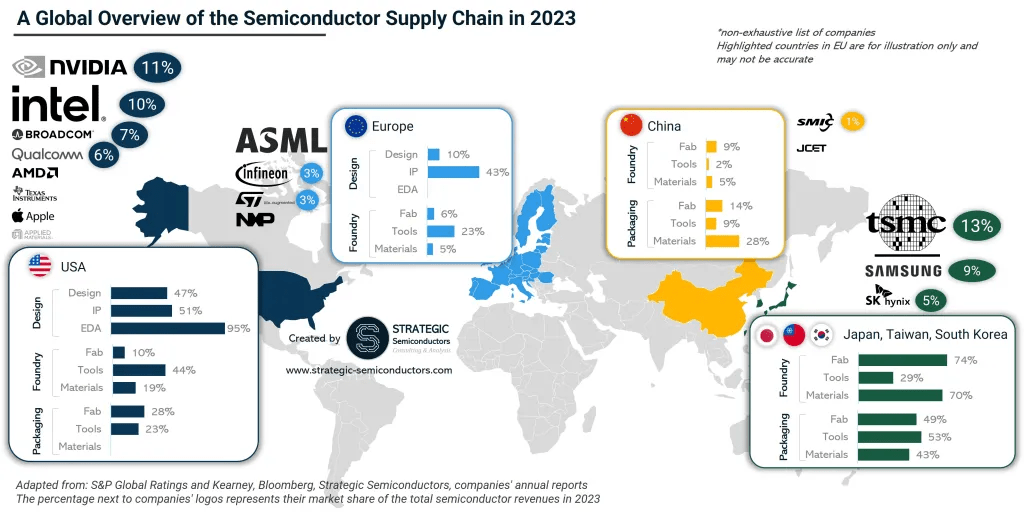
Taiwan currently holds 60% of the global semiconductor market share and a staggering 90% of the specialized chips market share. It houses a multitude of semiconductor companies proficient in every manufacturing stage, from design to testing. Taiwan also boasts state-of-the-art manufacturing facilities, some capable of producing semiconductors unavailable elsewhere in the world.
The United States saw a decline in its global semiconductor manufacturing share from 37% in 1990 to 10% in 2022. To address this, the CHIPS Act was enacted in 2022, allocating substantial funds to revitalize semiconductor production within the country. Despite this shift in manufacturing, American fabless semiconductor companies continue to excel in chip design, maintaining their dominance in the industry.
China’s plan to build 18 new fabs in 2024 highlights the government’s commitment to fostering domestic chip development. Moreover, the successful production of high-end chips, such as the autonomous-driving chip NX9031, underscores China’s competitiveness in the global semiconductor arena, despite facing geopolitical challenges.
Chips will be the foundation of AI
The advancement of artificial intelligence heavily relies on the evolution of AI chips. The AI chips are further classified into 3 categories – GPUs, FPGAs, ASICs, all of which differ in their hardware and functionality. These specialized computing hardware components are pivotal in both the development and implementation of AI systems. With the increasing sophistication of AI, there arises a corresponding need for enhanced processing power, speed, and efficiency in computing devices. AI chips play a critical role in meeting these escalating demands.
AI Chips will be used for development of Large Language Models (LLM), Robotics, Autonomous vehicles, Edge AI and an array of other innovative applications. These specialized hardware components are poised to revolutionize the way we interact with technology, enabling advancements in natural language processing, intelligent automation, adaptive robotics, real-time decision-making at the edge, and beyond.
Currently, Nvidia stands as a major player in AI hardware and software, commanding approximately 80% of the global market share in GPUs. Despite this dominance, Nvidia does not manufacture its own chips; instead, it relies heavily on Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Corporation (TSMC), which holds a staggering 90% share in producing the world’s advanced chips. TSMC serves as the primary supplier for AI chips used by Nvidia, further solidifying its foothold in the high-end chip market. Moreover, TSMC plays a pivotal role in producing core processors for Apple iPhones, Qualcomm mobile chipsets, and processors manufactured by Advanced Micro Devices, underscoring its significance in the semiconductor industry.
While generative AI tools like ChatGPT and Google Bard have popularized AI, the true innovation is occurring within enterprise organizations globally. Businesses are heavily investing in AI solutions, whether for commercial sale or internal enhancement of operations. Globally, companies plan to invest about $1 trillion in semiconductor fabs through 2030 whereas at the same time Companies like OpenAI are seeking trillions in funding for AI chip development, aiming to expand global chip-building capacity.
In conclusion, fostering collaboration in semiconductor development is crucial for preventing monopolies and ensuring equitable access to AI. Together, we can forge a more resilient and inclusive future for the semiconductor industry and drive innovation for the betterment of society.
“AI is the defining technology of our time, and semiconductors are its silent heroes, enabling machines to think, learn, and adapt.”
– Vedant Kale